Enumeration defines a set of variables related together. It also exists in other languages. Nonetheless, It does not behave in the same way as, for example, in C. That would only allow the enum types when declared. Note It is allowed since the Standard Fortran 2003. Check below how to declare them: How to use…
read moreAn allocatable array is the same as a dynamic array. Its size is not fixed therefore it is not known at compilation time. It is defined at execution time. It has several advantages compared to an explicit shape. The most important of all is its flexibility. It is also more memory efficient because it is…
read more
Abstract objects can have multiple implementations. Fortran does not offer a direct solution to declare them as an array. However, it is still possible to handle it. Check below how to do it: Abstract type: Several implementations: and Declare a dynamic array of concrete objects: Declare a dynamic array of the abstract type shapes: First,…
read moreAn abstract class is defined with the keyword abstract. It tells the class it cannot be instantiated. On the other hand, it can be used as shared behavior between related classes. That’s when a subclass is created by referring its parent. How to define an abstract class: Note two procedures are defined: getSpecies implementation is…
read moreElemental statement provides a simple and generic interface for a procedure regarding its rank -dimensions-. Due to Fortran strong typing programming style, It was a bit challenging to provide generic functions. It required to implement all possible forms (type and rank-dimensions-). Elemental focus in the rank issue with a simple interface. Note an elemental procedure…
read moreDue to Fortran being a strong type language It is required to have an implementation of the same algorithm for each type. Once done, it provides a generic subroutine. In order to achieve it in Fortran it is must be implemented in the following way: Finally: Output: ./a.out 5 11.0000000 15 No need to say…
read more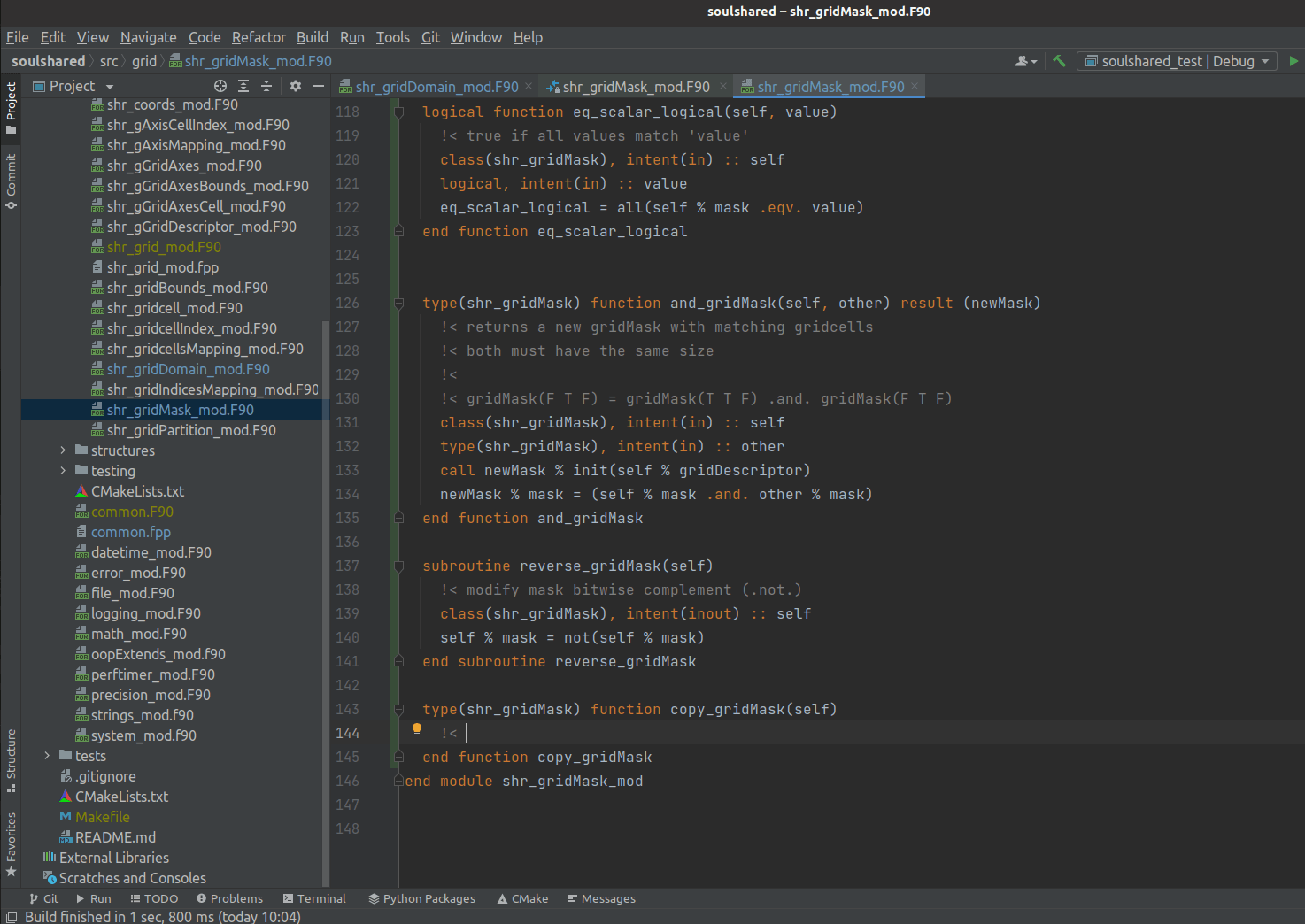
JetBrains-cLion is a non-open source (paying) IDE for C/C++. It has support for CMake, GIT, Refactoring and many other features. Because of the payment, there is a 30 days trial period. It is worth mention because it has a Fortran plugin. It enables the possibility to enjoy all features mentioned above in a very stable…
read more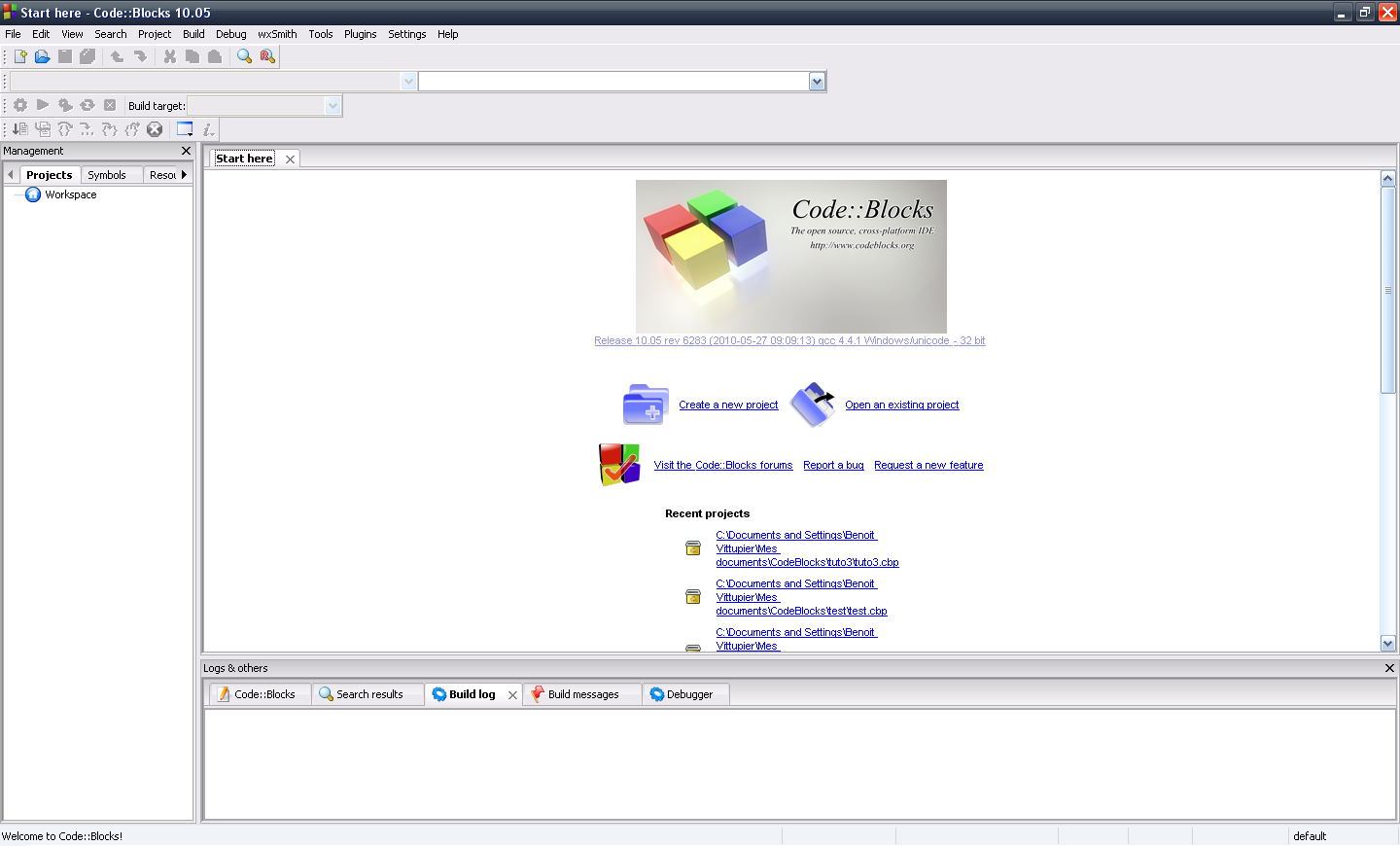
CodeBlocks is an open source Fortran IDE which runs on Linux and Windows. The application does not directly allow you to import a CMake project. However, it is possible to do it in a few simple steps. Check below the steps: # goto source project dir mkdir build cd build cmake -G”CodeBlocks – Unix Makefiles”…
read moreFypp preprocessor generates Fortran code based on Python language. However, in some cases it is not straightforward. Read below to discover how to create higher level functions. Let’s say our program requires to allocate an array for N supported ranks. dim is an array with the size of each rank. To make it possible We…
read moreOverloading a subroutine means to redefine its internal functionality for a customized behavior. Overall it adapts the class new characteristics to already wide-spread Fortran functionalities (==, =, + ,-, …). Specifically, this post only focus on the operators (+,-,*,/). In the following example, mynumber is generic class to hold any type of an integer number.…
read more-
« Previous
1
2
3
Next »